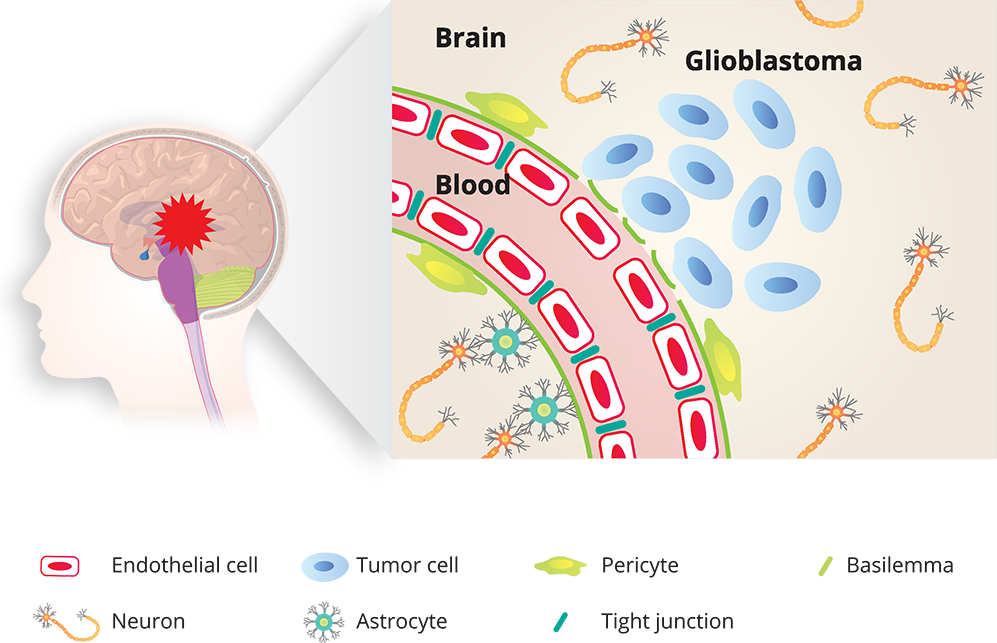
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) (also called glioblastoma) is a fast-growing glioma that develops from star-shaped glial cells (astrocytes and oligodendrocytes) that normally support the health of the nerve cells within the brain.
GBM is often referred to as a grade IV astrocytoma. These are the most invasive type of glial tumors, rapidly growing and commonly spreading into nearby brain tissue.
GBM can arise in the brain “de novo” or evolve from lower-grade astrocytomas or oligodendrogliomas. In adults, GBM occurs most often in the cerebral hemispheres, especially in the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain. GBM is a devastating brain cancer that typically results in death in the first 15 months after diagnosis.